RAN Protocol Stack (Part-3)
For Part-1 of RAN Protocol Stack :
https://tomar102003.blogspot.com/2022/09/ran-protocol-stack-overview-part-1.html
For Part-2 of RAN Protocol Stack :
So , in part 2 we have discuss till the MAC Layer now we have to discuss PHY Layer which is left in User-Plane , RRC Layer and NAS Layer of Control-Plane as all left layer of Control-Plane are same as User-Plane which we have discussed already in part-2 of this series.
1.PHY(Physical) Layer :
Source -techplayon.com
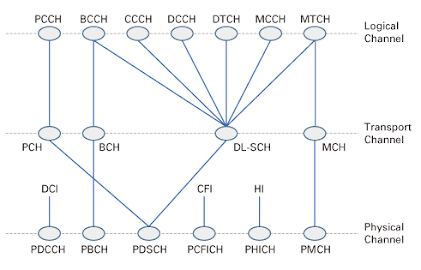
As you can see in above image that Physical Layer getting its services from the Transport Channel(which is a part of MAC Layer) ,hence getting services from MAC.
So first take a look on the Physical channels:
- PDCCH (Physical Downlink Control Channel) :This channel is used for downlink control information like scheduling sessions.
- PBCH (Physical Broadcast Channel) : This channel have the system information which is used by UE for getting the MIB(Master Information Block).
- PDSCH(Physical Downlink Shared Channel) : This is the main Channel through which paging and data which is sending from the network to the UE(User Equipment) , such as system information.
- PUSCH(Physical Uplink Shared Channel) : This is the main channel for the devices to send uplink data to the network.
- PUCCH (Physical Uplink Control Channel) : This is the channel through which Hybrid ARQ Acknowledgement send from the device side to the network regarding the transport blocks which is send from the network to device side.
- PRACH (Physical Random Access Channel) : This channel is used for physical random access procedures.
Functions of Physical Layer are as follows:
- CRC(Cycle Redundancy Checks) : This checks is used for error detection as some redundant bits are add up to the data for checking at the receiver side as its get any error or not in transmissions. Its checks the transport blocks through the generator polynomial which is generated at the sender side, as redundant bits are calculated using this generator polynomial.
- LDPC(Low Density Parity-Check) : This check is used for error correction as error has already detects by the CRC .Its uses two parameters.
- Transport Block Size(TBS)
- Code Rate
Now if TBS and Code Rate are above the threshold(Minimum) then Base Graph 1 will used for LDPC , otherwise Base Graph 2.
If Transport Block size is greater than it is breakdown into code blocks and each code block is go through LDPC coding .
So , this gives us a benefit of not retransmitting the message or data on found of error as LDPC correct it but in some cases when whole transport block get corrupted then there will be a case of retransmission of the data.
- Rate Matching : This is used for transmitted the extract set of bits from each code block in a given interval of time as all bits cannot be transmitted at the same transmitted time .
- Scrambling : This is used for as UE is hearing signals from many gNBs(RAN) , So Scrambling code block is multiplied by Scrambling Sequence and which device have this Scrambling Sequence can hear the signal corresponding to that gNB only and all other signal will be treated as interference to the UE.
- Modulation : This is for modulation of the scrambled bits from 1's and 0's to a complex modulated symbols. Each Symbols give 'n' bits depending on the used modulation scheme. Some Modulation Scheme are QPSK, 16 QAM ,64 QAM , 256QAM .
- Layer Mapping : As in 5g NR , special multiplexing is used , so it is possible to transmitted multiple layer of data through multiple antenna terminology.
- Antenna Mapping : As different layers of data are there so we have to mapped virtual antenna ports . Pre-Coding matrix is used for mapping the different numbers of layers into the corresponding virtuals ports .
Now physical antenna are more than the virtuals antenna so linear mapping is done from virtual antenna ports to physical antenna ports .
2. RRC-NAS (Radio Resource Control )-(Non-Access Stratum)
Functions of RRC (UE-gNB) :
- Broadcast of System Information
- Radio Bearer Establishment
- Connections Establishment and release Functions
- Paging
There are three types of RRC modes in NR :
- RRC-Idle
- RRC-Inactive
- RRC-Connected
 |
| Source -ScienceDirect.com |
when device is turned on for the first time so it is in RRC-Idle mode and when it is connected to the network it is in RRC-connected mode and communications happen between the device and the network.
Now RRC context is stored both in UE and gNB when there is no communication it has to go RRC- Idle mode again so to save battery . After that when it want to come again in RRC-Connected mode , it has to do a lot of Control-signaling. So there is a introduce of RRC-Inactive mode which stored the RRC context and UE can also go to sleep for energy saving . Thus this mode have resolved the issue of going again and again for Control-signaling and give benefits of both performance and energy efficient .
There is RRC-Suspend and RRC-Resume for suspend from connected mode to inactive mode and from inactive to connected mode respectively.
Functions Of NAS (UE-AMF) are as follows:
- Authentication and Security
- Idle Mode Enabling Paging
- Session and mobility management
AMF here is Access and Mobility Function which is a part of 5g core network . We will see its function in 5g Core networks series.



Comments
Post a Comment