RAN Protocol Stack (Part-2)
For Part-1 of RAN Protocol Stack :
Below Image give you the overview about what we describe above.
As you can see that QoS Flow are giving their QFI for differentiate between different quality of service within a PDU Session.
If there is large transport block then it divided into Code Block Groups(CBG) and if particular data is getting NAK then we transmits particular CBG instead of transmitting the whole transport block.
If there are some users connected to the same gNB then how things are scheduled so that each one of them get data , so scheduler make decision according to the above three mentions categories , so it get by this which user will serve first and in a preemptive way and so on.
In the below image, we have all layers of User Plane Protocol Stack . Now From top to bottom, we will go through each layer with wide description of each functions within each layer.
Functions of this layer are :
- QoS ( Quality of Service ) Flow Handling : This layer mapped the quality of service , QFI (Quality of Service Flow ID) to the appropriate radio bearer between the gNodeB (RAN) and the UE (User Equipment or Device).
QFI(Quality of Service Flow ID): It is used to differentiate between different quality of service within the PDU's (Protocol Data Unit) Sessions.
Below Image give you the overview about what we describe above.
 |
| source - techplayon.com |
All Quality of service are grouped together in a GTP-U N3 tunnel which is between the gNodeB (RAN) and the UPF(User Plane Function).
Now , you can see in the above image that QFI -1 and QFI - 2 is mapped within the same radio bearer, as it is the works of SDAP.
If one QFI is for whatsapp video call and another QfI is for zoom video call so SDAP mapped these QFI in the same Radio Bearer and other QFI such that Youtube Videos such that live streaming than it mapped this is different Radio Bearer.In some Cases , there will be different PDU Session also .
Now we have three different types of Quality of Service :
- GBR(Guaranteed Bit Rate) : This is defined for the applications which required Guaranteed Bit rate .
- Non-GBR(Non Guaranteed Bit Rate): This is where traffic is bursty in nature.
- Delay Critical : This is used for the critical applications.
2. PDCP(Packet Data Convergence Protocol) :
Functions of this layer are :
- Header Compression : As when control Information is add up with the data Packets such that IP address IPv4 or IPv6 , the size of data packets increase , so to reduce the size header compression is needed .
ROHC (Robust Header compression) which is an algorithm used to compress headers of various IP Packets.
- Ciphering and Integrity Protection: Ciphering is to encrypt the data so that third party cannot understand what is going and from and where it is going . This is used to prevent Eavesdropping.
Integrity protection is used to verify that the data originated from the right source .
- Routing and Duplication of Split-Bearers : As UE is connected to different gNB then we split and duplicate the data so as to maintain quality of services by sending some data to one gNB and some data to other one.
- In Sequence-Delivery : The data packets are provided with a sequence number so that PDU's stored in Buffer until all previous PDU's are received.
3. RLC (Radio Link Control):
Functions of this layer are :
- Segmentation: Data is divided into segment so as to make data size that it can go through transport block.
- ARQ (Automatic Repeat Request)- Retransmission : This is used to retransmit the data packets when there is a negative acknowledge from the receiver's end.
Three different RLCs Modes:
- Transparent mode : No Segmentation , No Duplicates Removal ,No Retransmission .
- UnAcknowledged mode : No Retransmission, but Segmentation.
- Acknowledged mode: Retransmission and Segmentation , Duplicated detection and removal.
4. MAC (Media Access Control) :
As each layer provide and get services from above and below layers.
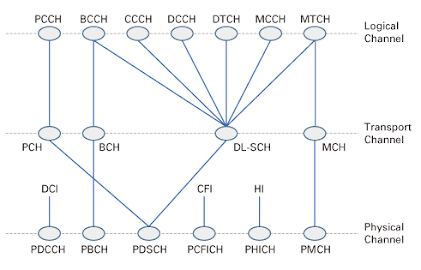
MAC layer provides services to RLC layer in form of Logical Channels and uses the services of Physical (PHY layer) in form of transport layer.
Logical Channels : These Channels are defined as what type of information they carries. Logical Channels can be one of the two groups
- Control Channels : These Channels are used to transmit and configure the data necessary for operating in our system.
- Traffic Channels : These channels are used to transfer user plane data.
Logical Channels in the above image are as follows:
- PCCH (Paging Control Channel )
- BCCH (Broadcast Control Channel)
- CCCH ( Common Control Channel)
- DCCH ( Dedicated Control Channel)
- DTCH ( Dedicated Traffic Control Channel)
Transport Channels in the above images are as follows:
- PCH (Paging Channel)
- BCH (Broadcast Channel)
- DL-SCH (Downlink Shared Channel)
- UL-SCH (Uplink Shared Channel)
Carrier Aggregation:
This terms is used in to increase data rate per user which directly increase the frequency blocks (component carriers) assigned to a user.
Functions of this layer are :
- HARQ(Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request): This is combination of High rate Forward Error correction (FEC) and ARQ retransmission on error data.
This function of MAC layer check for error messages in a pool of received messages and retransmits them through the scheme of ARQ on the sender side .
Until sender get Negative Acknowledgement(NAK) regarding the particular data , sender will retransmit it until it will not get NAK.
 |
| source- techplayon.com |
- Scheduling : This is used to allocate the resources depending upon the following three factors:
- Data Connections
- Data Priority
- Buffer Status
 |
| source - 5G | sharetechnote.com |
If there are some users connected to the same gNB then how things are scheduled so that each one of them get data , so scheduler make decision according to the above three mentions categories , so it get by this which user will serve first and in a preemptive way and so on.




Comments
Post a Comment